Followed by the post below.It’s easier to understand if you look at the previous two posts.
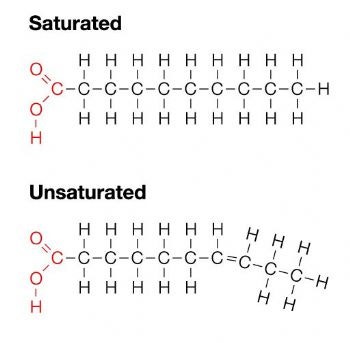
The difference between saturated fat, unsaturated fat, trans fat and organized food, I’ve heard of a lot of saturated fat, unsaturated fat, trans fat. Good fat, bad fat…blog.naver.com
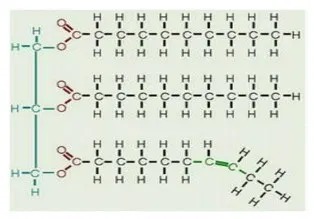
The difference between saturated fat, unsaturated fat, trans fat and organized food, I’ve heard of a lot of saturated fat, unsaturated fat, trans fat. Good fat, bad fat…blog.naver.com
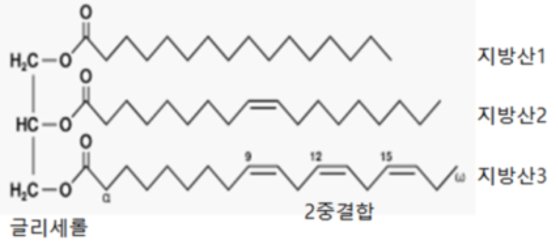
The difference between saturated fat, unsaturated fat, trans fat and organized food, I’ve heard of a lot of saturated fat, unsaturated fat, trans fat. Good fat, bad fat…blog.naver.com

Unsaturated fatty acids are known as good fatty acids, and they have the famous omega series.
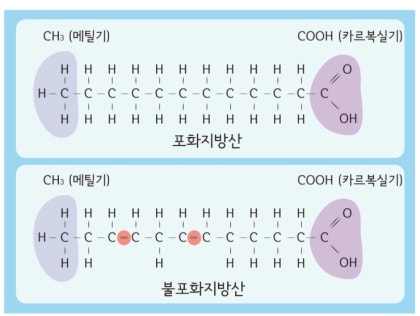
Omega
Among the unsaturated fatty acids, omega 3, 6, and 9, omega 3 and 6 are essential fatty acids that need to be consumed because they are not synthesized in the body.

[Omega 3] Omega 3 is a ingredient that has been recognized for its functionality and is also manufactured as a health functional food. It’s EPA and DHA among Omega 3.There are various functions such as improving blood triglycerides, improving blood flow, improving memory, and improving dry eyes.Omega-3s are especially high in blue-backed fish, seaweed.[Omega 6] Omega 6 is much higher in most foods than Omega 3, so many people usually take it too much.Although omega-6 is consumed excessively, only gamma-linolenic acid, which is difficult to consume directly from ordinary foods, is consumed separately as a health functional food.Omega-3 and 6 intake ratesBoth of these are essential fatty acids, but the problem is that we consume too much omega-6.The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends a maximum omega-3: omega-6 = 1:4, but for most diets, omega-6 intake is 10 to 14 times higher than omega-3.The high percentage of omega-6 intake itself can be a problem.Effect of intake rateSo how does the ratio of omega-3s and omega-6s affect?1. Omega-3 Competing Omega-3 and Omega-6 follow the same physiological pathway.Excessive intake of omega-6 can interfere with the absorption and function of omega-3.Omega-3s, along with their various health benefits, also suppress the side effects of Omega-6.Conversely, disproportionate overabsorption of omega-6 inhibits omega-3.2. Inflammation Omega 3 and 6 both have anti-inflammatory properties, but Omega 6 is also contagious on the contrary.Omega 6 also means that it stimulates inflammation.The higher the percentage of omega-6 intake, the higher the risk of chronic inflammation and metabolic syndrome, and the lower the percentage of omega-6 intake, the lower the risk of inflammation. [1][2]3. 3. Cardiovascular disease The high rate of omega-6/mega-3 may increase cardiovascular disease.The lower the rate of omega-6/3, the lower the mortality rate of cardiovascular disease.[3]The lower the rate of omega-6/3, the lower the blood clot, which is a factor that lowers the risk of cardiovascular disease.[4]4. The lower the rate of cancer omega-6/3, the lower the colon cancer cell proliferation, and the lower the risk of breast cancer.[3][6]The lower the rate, the lower the risk of prostate cancer.[5]5. Obesity?Some studies have shown that the higher the intake of omega-6 among unsaturated fatty acids, the higher the risk of obesity.Omega can increase cell membrane permeability to increase fat accumulation by increasing triglyceride content.[7][8]Unsaturated fatty acids are fatty acids with double bonds.The more you have multiple bonds, the faster the oxidation rate, and the faster the oxidation rate of omega-6 among unsaturated fatty acids, the higher the oxidation stress.This oxidative stress causes a number of side effects.arrangementThe percentage of omega-3 and 6 intake is more important than omega-6 being a bad substance.In modern times, when omega-6 intake is 10 times higher than omega-3, we need to increase our intake of omega-3.The maximum w3:w6=1:4 recommended by the World Health Organization is recommended to reduce the intake rate to 1:1, if possible.[1]The importance of low Omega-6/Omega-3 ratio (2) to reduce the importance of high-temperature and low-temperature of natural acid (3] Omega-6/Omega-3) Omega-3The increase of obesity and Omega-3/Omega-3/Omega-3 fatty acid ratio of Polish population breast cancer[1]Importance of Maintaining Low Omega-6/Omega-3 Ratio for Reducing Inflammation[2]Health Effects of High Diet Omega-6/Omega-3 Essential Fatty Acids [3]Omega-6/Omega-3 Ratio and Low Omega-6/Omega-3 Ratio for Reducing Platelet Aggregation, Coagulation, and Thrombosis[5]Risk of Omega-6/Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Prostate Cancer in Dietary Health Study Populations[6]Total Dietary Fatty, Fatty Acids and Omega-3/Omega-6 Rates Risk Factors for Polish Population Breast Cancer – Case-Control Study [7]Increase in Omega-6/Omega-3 Fatty Acid Rates Increase Risk of Obesity [8]Early Origins of Omega-6 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids and Obesity
